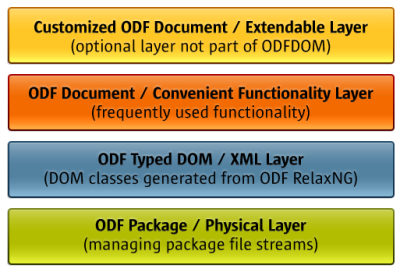
The ODFDOM project's objective is to provide an API for easily reading, writing and manipulating ODF documents. ODFDOM implements a layered approach through which documents are accessed.
- The ODF Package / Physical Layer - provides direct access to the resources that are stored in the ODF package, such as XML streams, images or embedded objects.
- The ODF Typed DOM / XML Layer - provides classes for all XML elements, with their XML attributes mapped to class attributes. It is a typed DOM as every ODF XML element is represented by their own class, generated from the ODF RelaxNG schema. This level is concerned with the representation of the content of the standardized XML streams of the underlying package using the language independent W3C DOM API. This layer easily provides the ODF developer with all informations about the ODF XML structure.
- The ODF Document / Convenient Layer - represents components consisting of multiple underlying XML elements. This level is concerned with usability aids, which are not specified by the ODF standard.
- The Customized ODF Document / Extendable Layer - is not part of the delivered API, but part of the design. This level is concerned with user defined customizations.
The ODFDOM Layers
The ODF Package / Physical Layer
At this level, a document is represented as a package of named resources. For standardized file streams explicit methods are being provided.
The file streams are similar for all ODF documents.
The main requirements for this layer are:
- Zip/unzip the file streams of the package
- Enlist all file streams in the /META-INF/manifest.xml (otherwise OOo won't save the file streams)
- Begin the package with an unzipped 'mimetype' file stream
All sources of the Package/Physical layer are organized beyond org.odftoolkit.odfdom.pkg.*
The ODF Typed DOM / XML Layer
At this level, all XML file streams of the document are accessible via the W3C DOM API, but only the ODF standardized XML file streams of the document their own classes representing their ODF XML. Foreign XML within a specified ODF file remains in general in the document model and won't be neglected unless desired ( which might be a future option).
For instance the following pictures shows the mapping of a XML structure of an ODF table to a
W3C derived ODF DOM class structure.
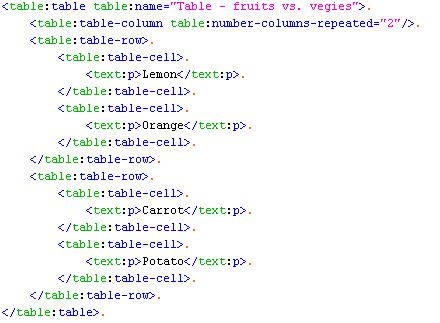
xml structure
|
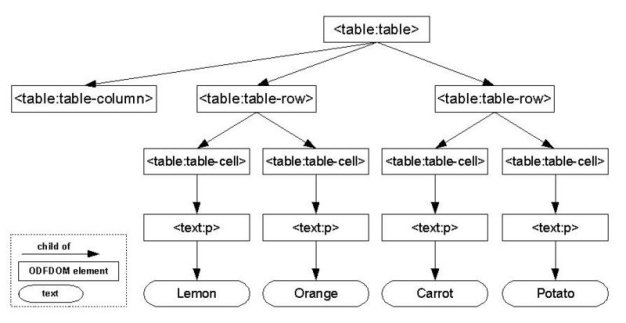
ODF DOM class structure
|
All sources of the typed DOM/XML layer are organized beyond org.odftoolkit.odfdom.dom..
Its sources are - with a few exception - automatically generated from the ODF 1.2 RelaxNG schema using the following naming conventions:
- The Class name is equal to the element local name using the OOo Namespace as an Prefix and 'Element' as Suffix.
- Elements are stored beyond 'element' and a sub-package equal to their Namespace used by the OOo.
- Attributes are stored beyond 'attribute' and a sub-package equal to their Namespace used by the OOo.
For instance, the frame element 'draw:frame' would be generated as class org.odftoolkit.odfdom.dom.element.draw.DrawFrameElement
The following example illustrates how to add a graphic to the ODF document, that it is viewable:
The ODF Document / Convenient Functionality Layer
The purpose of a class from the convenient layer is a higher usability for the API user. Usually a class is derived from covered XML layered class.
All sources of the ODF document / convenient functionality layer are organized beyond org.odftoolkit.odfdom.doc.* The name of a convenient class is similar as it's XML parent, adding an 'Odf' prefix, but neglecting the 'Element' suffix.
Furthermore, have naming abreviation been neglected.
for instance, a convenient class for a paragraph element 'text:p', derived from the class representing 'draw:frame' would be named org.odftoolkit.odfdom.doc.text.OdfTextParagraph
In contrary to the classes of the XML layer, an object of the convenient layer controls multiple XML elements. For instance, a default table consisting of the similar amount of the earlier mentioned table can be created by a single method call, instead creating every single element using directly the XML layer.
The Customized ODF Document / Extendable Layer
Although not part of the ODFDOM package it is designed as a layer on top of ODFDOM, where customer are able to replace/overwrite/customize ODF elements.
For instance, change the default size/style of their new tables.
Further Information
For further Information about ODFDOM and related topics please visit following pages:
- ODFDOM wiki
- ODF Specification 1.1
- ODF Specification 1.2 (community draft 2 revision 3)
- ODF Specification 1.2 (community draft 2 revision 3) [LOCAL COPY]




